Orthopedic Injuries
Shoulder / Upper Arm Fractures
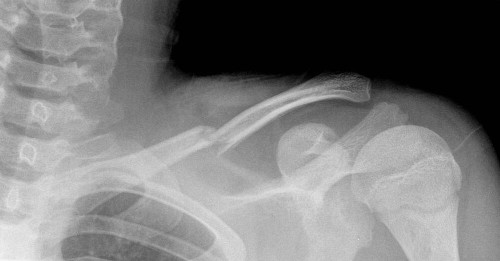
Clavicle Fractures
Immobilization
- For medial/proximal fractures at risk sternoclavicular joint involvement/posterior displacement, consider CT scan, including CTA for large vessel involvement
- Sling and ACE wrap or
- Pin sleeve to opposite shoulder (infants) or can provide gentle “figure 8” ACE wrap around shoulders
Follow Up
- All follow up with Ortho regardless of degree of angulation (management is usually non-operative, surgeon preference)
- No call to Ortho needed for any fractures unless there is at-risk skin
Mid-shaft clavicle fracture
Shoulder Dislocations
Immobilization
- Sling and swathe after reduction
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Medicine if first dislocation
- Follow up with Sports Medicine or Ortho if recurrent dislocation
Anterior shoulder dislocation

Proximal Humerus Fractures
Immobilization
- Sling and Swathe or
- Abduction Pillow if available
Follow Up
- Consider discussion with ortho if >50% translated and/or >30 degrees angulation, >1 cm separation, any rotational deformity, or intrarticular fracture
- Consider discussion with Ortho if patient >10 years of age
Proximal humerus fracture
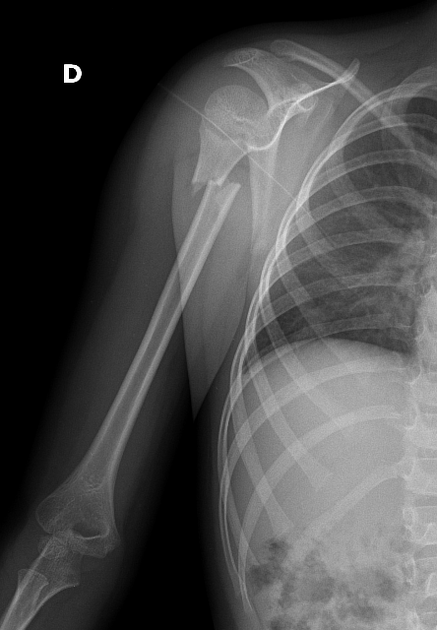
Humerus Shaft Fractures
Immobilization
- Sling and Swathe
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
- Call Ortho in the ED for rotational deformity
Humerus shaft fracture
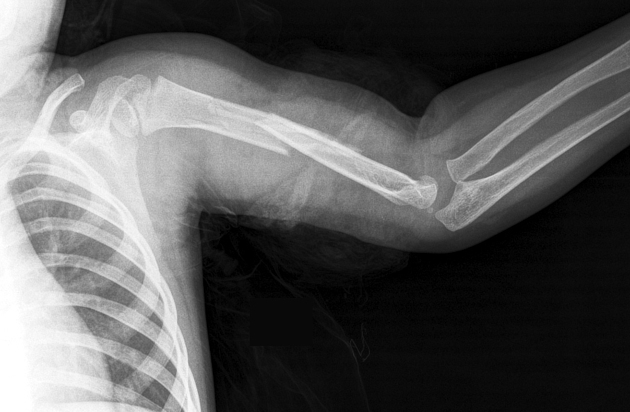
Elbow Fractures
Lateral Condyle
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint (elbow at 90°)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
- Call Ortho in the ED for any displacement/dislocation
Lateral condyle fracture

Medical Epicondyle
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint (elbow at 90°)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
- Call Ortho in the ED for any displacement/dislocation
Medial epicondyle fracture

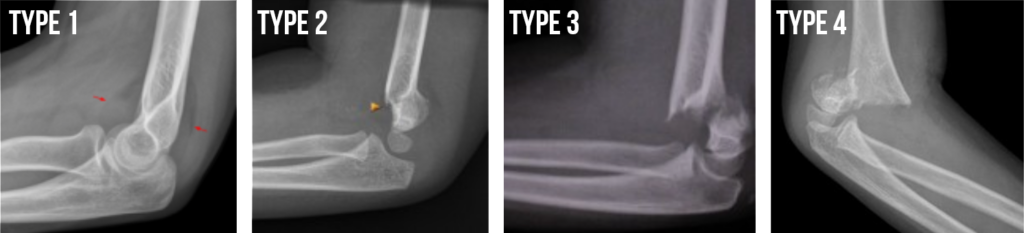
Supracondylar Fractures of the Humerus
Type 1 Non-displaced
Immobilization
- Long arm posterior splint
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Types 2, 3, & 4
- Type 2 is displaced in 1 plane
- Type 3 is displaced in 2 or 3 planes
- Type 4 has complete periosteal disruption
Immobilization
- Long arm posterior splint in position of comfort
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho, can discuss whether direct admit to Base is appropriate if at Liberty (concerns of adequate pain control from ED to admission)
Supracondylar Humerus Fracture Types
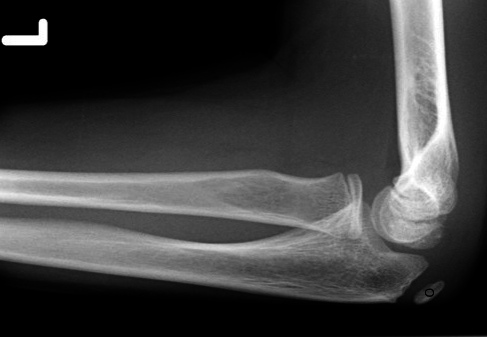
Olecranon
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint (elbow in slight extension)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
- Call to Ortho only if associated dislocation/displacement
Olecranon fracture
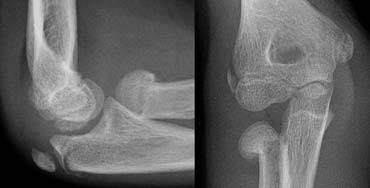
Radial Head/Neck
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint (elbow at 90 degrees) with sling & swathe
Follow Up
- Call Ortho for any radial head fracture, additional imaging may be needed
- Call Ortho for radial neck fracture 10 degrees or more, measurements can be difficult and they should assess directly
Radial head fracture

Radial neck fracture
Monteggia Fracture
Proximal ulna fracture with associated radial head dislocation
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint in position of comfort
Follow Up
- Call Ortho in the ED
Monteggia Fracture
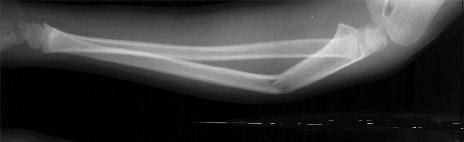
Little League Elbow
Overuse Injury
Immobilization
- Limit activity – do not immobilize
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med
Forearm Fractures
Distal Radius Buckle (Torus) Fracture
Immobilization
- Velcro wrist splint
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho to assure it isn’t a physeal fracture
Buckle Fracture
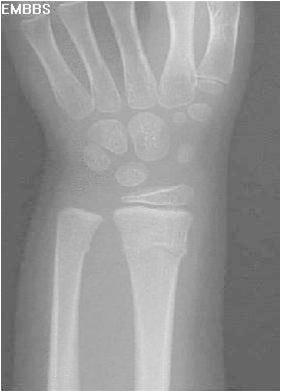
Radius & Ulna Fractures
Immobilization
- Sugar Tong splint
Follow Up
- Call Ortho for
- Any rotational deformity
- Dorsal angulation 10-15 degrees or greater (may recommend molding with pain medication for lower angulation)
- For less than 10 years, call for:
- Extension angulation 15-20 degrees
- Flexion angulation 10 degrees
- Radial ulnar deviation 10 degrees
- For 10 years and older, call for any angulation greater than 10 degrees
Both Bone Forearm Fractures
Galeazzi Fracture
Distal radius fracture with disruption of distal radioulnar joint
Immobilization
- Long-Arm Posterior Splint in position of comfort
Follow Up
- Call Ortho in the ED
Galeazzi Fracture

Hand Fractures
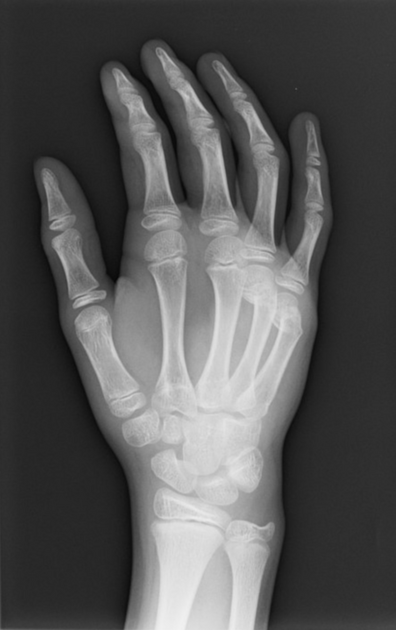
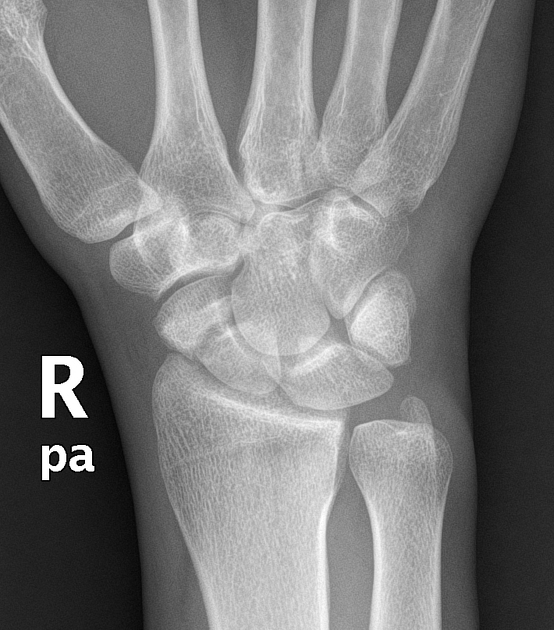
Scaphoid Fracture
Immobilization
- Thumb spica splint
Follow Up
- All definite or suspected follow up with Hand
- Displaced more than 1mm should get a CT in the ED for possible surgical planning
Scaphoid Fracture
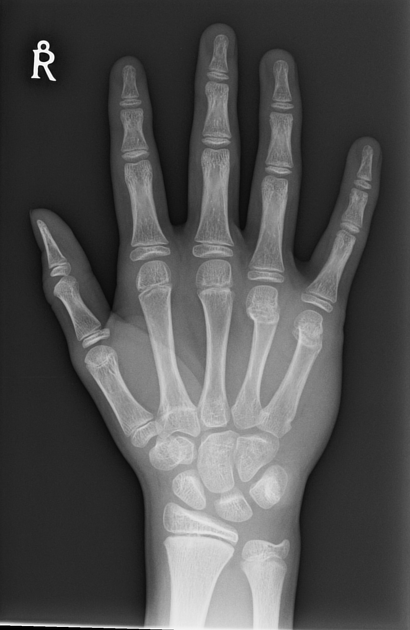
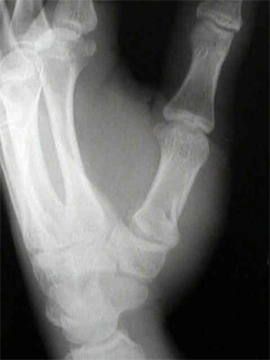
First Metacarpal
Immobilization
- Thumb spica splint
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any clinical deformity or displacement
- Intraarticular fracture (Bennett or Rolando) often needs CT scan for possible surgical planning
First Metacarpal Fracture
Second Metacarpal
Acceptable angulation: Neck <20°, Shaft <10°
Immobilization
- Radial gutter splint
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any clinical deformity, any rotational deformity, or angulation above acceptable limits – Many can be reduced and casted in clinic if >10 years old
- Follow up with Hand
Second Metacarpal Fractures
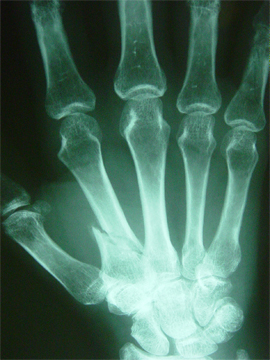
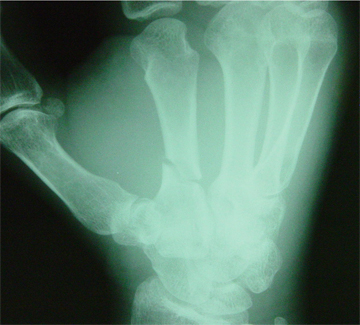
Third Metacarpal
Acceptable angulation: Neck <30°, Shaft <10°
Immobilization
- Ulnar gutter splint
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any clinical deformity, any rotational deformity, or angulation above acceptable limits – Many can be reduced and casted in clinic if >10 years old
- Follow up with Hand
Third Metacarpal Fracture
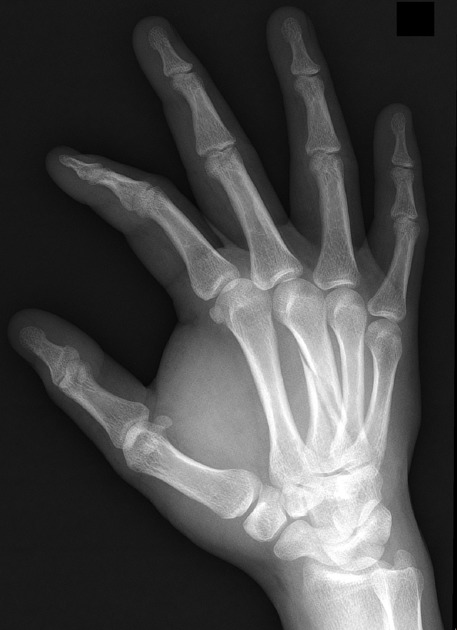
Fourth Metacarpal
Acceptable angulation: Neck <40°, Shaft <20°
Immobilization
- Ulnar gutter splint
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any clinical deformity, any rotational deformity, or angulation above acceptable limits – Many can be reduced and casted in clinic if >10 years old
- Follow up with Hand
Fourth Metacarpal Fracture
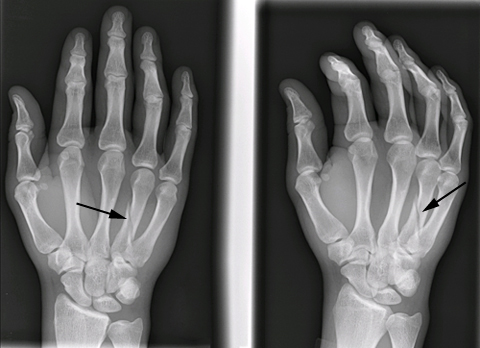
Fifth Metacarpal
Acceptable angulation: Neck <50°, Shaft <30°
Immobilization
- Ulnar gutter splint
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any clinical deformity, any rotational deformity, or angulation above acceptable limits – Many can be reduced and casted in clinic if >10 years old
- Follow up with Hand
Fifth Metacarpal Fracture
Finger Injuries
Phalangeal Neck Fracture
Any Finger
Immobilization
- Appropriate splint for the affected finger
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for any angulation, clinical deformity (especially rotational), or displacement
Phalangeal neck fracture
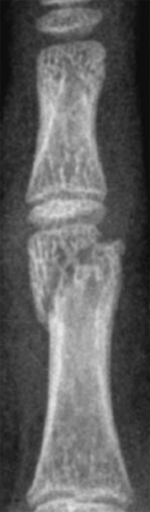
Thumb Fractures
Immobilization
- Thumb spica splint or cast
Follow Up
- Call to Hand for:
- Any rotational deformity
- Angular deformity >10°
Thumb fracture

Phalanx Fracture
First through fifth digits
Immobilization
- Appropriate splint for the affected finger
- Radial gutter for index/long
- Ulnar gutter for ring/small
- Buddy Taping as indicated
Follow Up
- Call to Hand
- Any rotational deformity
- Angular deformity >10°
- Open fracture EXCEPT tuft
- Follow up with Hand:
7-10 days for tuft and buckle fx
All other injuries, 3-7 day
Salter Harris II Fracture
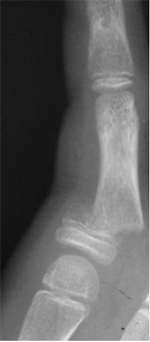
Seymour Fracture
Physeal fracture of distal phalanx with associated nailbed injury
Immobilization
- Appropriate splint for the affected finger
Follow Up
- Call to Hand to see in the ED
- Requires antibiotics upon discharge
Seymour Fracture
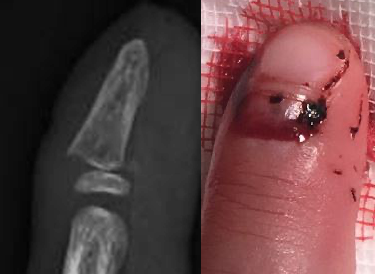
Jersey Finger
Flexor tendon injury
Immobilization
- Splint for comfort
Follow Up
- Call to Hand to see in the ED
Jersey Finger
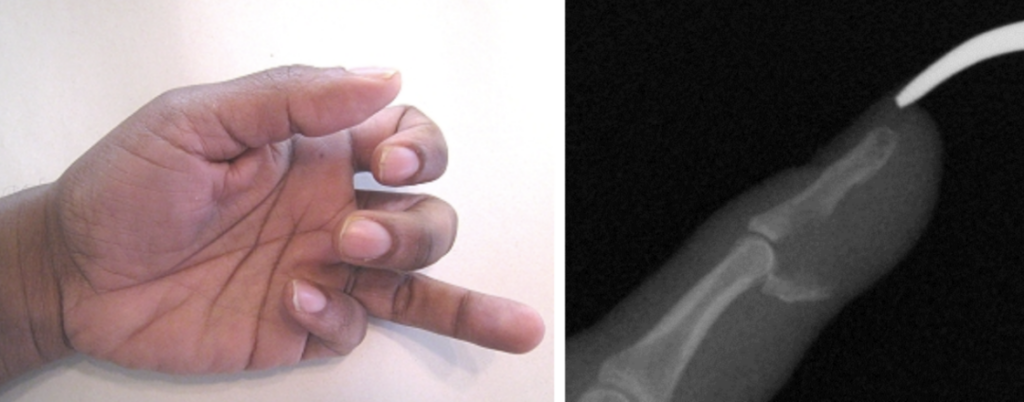
Mallet Finger
Extensor tendon injury
Immobilization
- Splint in extension
Follow Up
- Follow up with Hand
Mallet finger
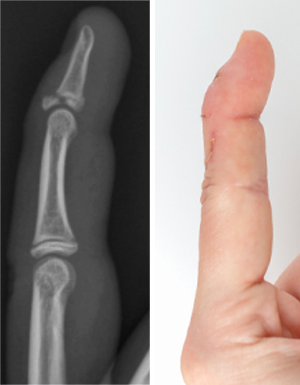
Volar Plate Avulsion
Immobilization
- Tray or aluminum splint
Follow Up
- Follow up with Hand
Volar Plate Injury
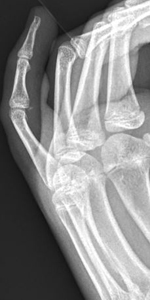
Phalangeal Dislocations
Dorsal PIP & DIP
Immobilization
- Aluminum Splint
Follow Up
- Attempt reduction in the ED – rarely associated with volar plate injuries that make reduction more difficult
- Follow up with Hand
Volar PIP & DIP
Immobilization
- Aluminum Splint
Follow Up
- Attempt reduction in the ED – unless associated with extensor tendon avulsion which requires Hand consult
- Follow up with Hand
MCP
Immobilization
- Thumb (1st): Thumb Spica Splint – MCP in slight flexion, IP joint free
- Index (2nd): Radial Gutter Splint – Wrist in 20–30° extension, MCP at 70–90° flexion, IP joints extended
- Middle (3rd): Radial Gutter Splint – Wrist in 20–30° extension, MCP at 70–90° flexion, IP joints extended
- Ring (4th): Ulnar Gutter Splint – Wrist in neutral to slight extension, MCP at 70–90° flexion, IP joints extended
- Small (5th): Ulnar Gutter Splint – Wrist in neutral to slight extension, MCP at 70–90° flexion, IP joints extended
Follow Up
- Attempt reduction in ED only if no fracture and experienced provider. Sometimes irreducible upon arrival.
- Do not apply longitudinal traction! – MCP dislocations are almost always dorsal and can become entrapped with longitudinal traction
- If proximal phalanx is angulated into extension, then it is typically simple
- If proximal phalanx is parallel with the metacarpal (but dorsally translated), there is often a volar plate entrapped, and Hand consult is needed
- Follow up with Hand
Nailbed Injuries
Proximal nailbed injury
Management
- Remove nail if nail root/matrix disrupted
- Repair laceration with absorbable suture
- Replace nail or stent with foil
- Secure with absorbable suture of the lateral nail folds
- Do not use glue
Follow Up
- Follow up with Hand
Proximal nailbed injury

Distal nailbed injury (including tuft fracture)
Management
- Nail removal only if indicated (can remove distal portion only), laceration repair and repair of nailbed with absorbable suture
Follow Up
- Follow up with Hand
Distal nailbed injury
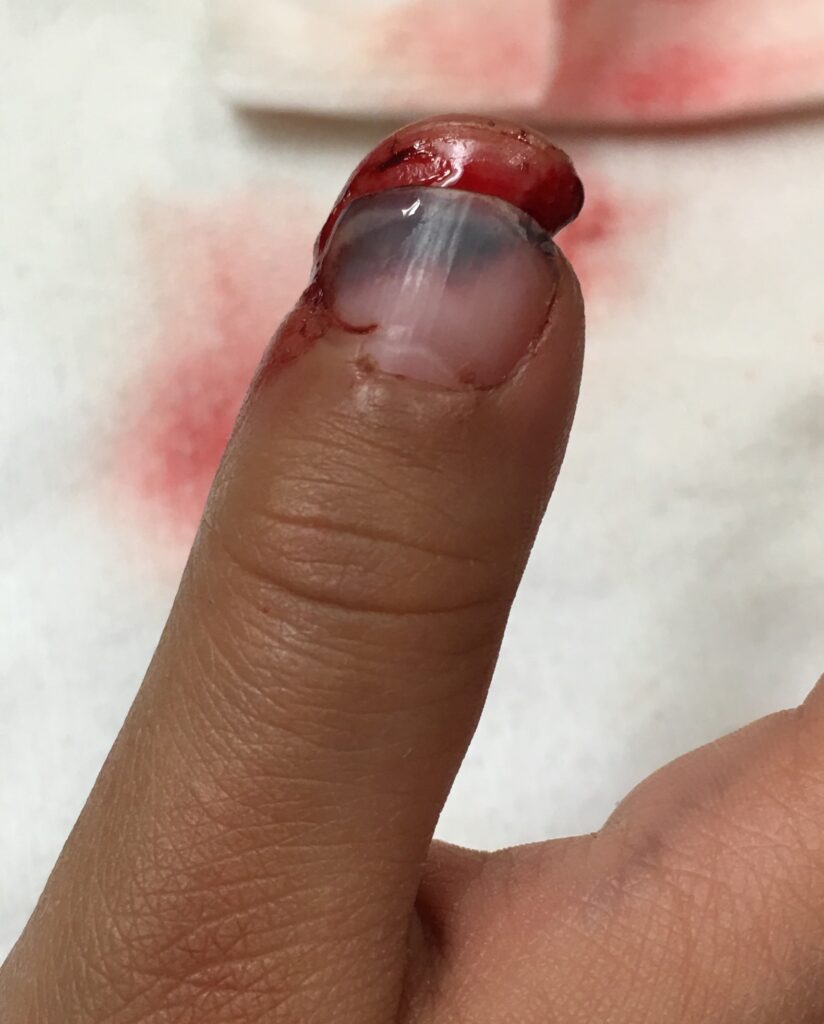
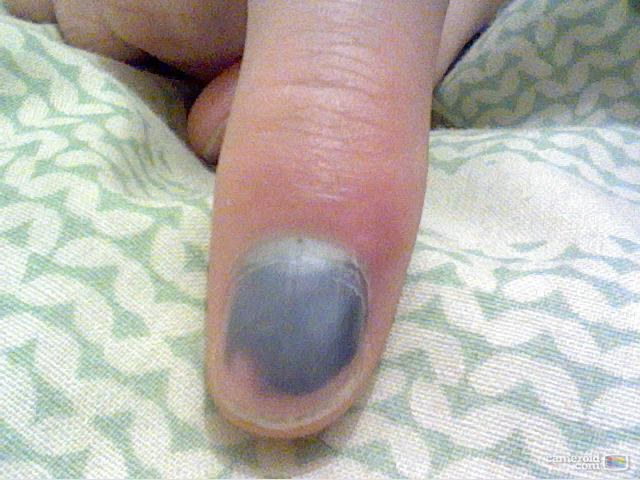
Subungual hematoma
Management
- Imaging to rule out fracture
- Trephination if 100% of nail surface or if painful
Follow Up
- Follow up with Hand
Subungual hematoma
Femur Fractures
Shaft
Immobilization
- Position of comfort & good circulation
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho
Femur shaft fracture

Distal Metaphysis
Non-Displaced
Immobilization
- Long leg splint (Non-weight bearing)
- Consider cast for very young children
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Distal femur physeal fracture

Knee Injuries
Patella Dislocation
Immobilization
- Knee immobilizer after reduction
- Weight-bearing as tolerated
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med or Ortho
Tibial Spine / Plateau Fracture
Immobilization
- Long-Leg Splint & crutches (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho
Trampoline Fracture
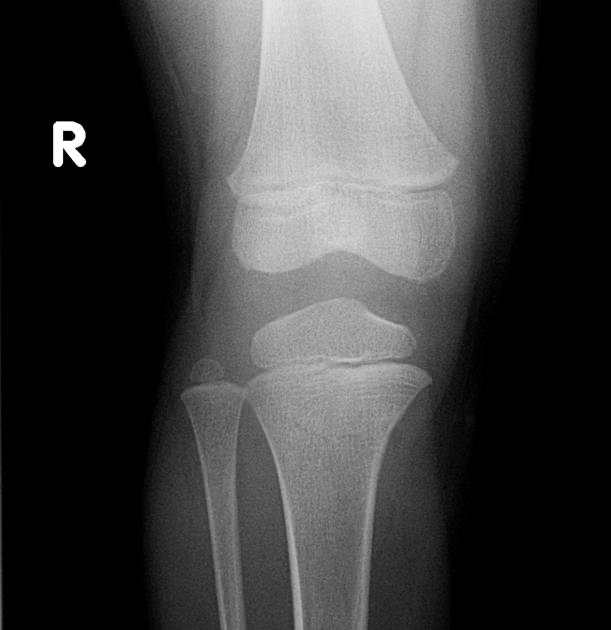
Tibial Tuberosity
Immobilization
- Long-Leg Splint or knee immobilizer (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho for type II-VI or ≥2 mm displacement
Tibial Tuberosity Fracture
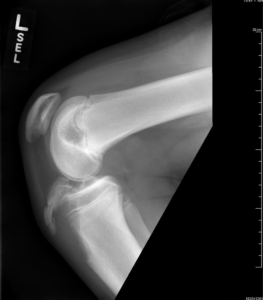
Ligament / Cartilage Injury
X-Rays Negative
Immobilization
- ACE wrap
- Non-weight bearing / toe-down weight bearing for balance only
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med or Ortho
Apophysitis of upper tibia or lower pole of patella
Osgood-Schlatter / Sinding-Larsen-Johansson syndromes
Immobilization
- No immobilization
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med
Osgood-Schlatter
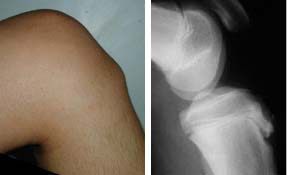
Sindig-Larsen-Johansson
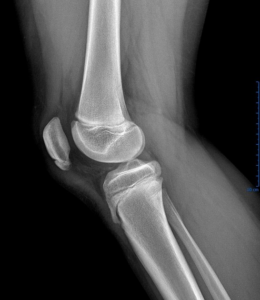
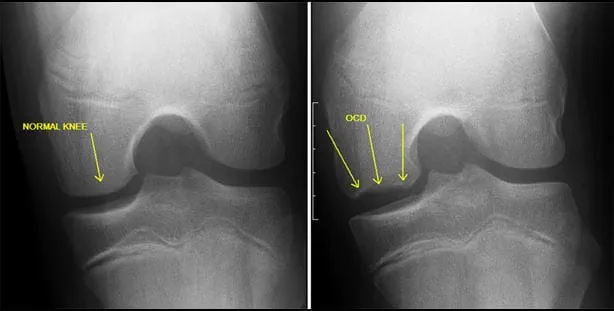
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Immobilization
- No immobilization
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med or Ortho for non-urgent MRI
Osteochondritis Dissecans
Tibia & Fibula Fractures
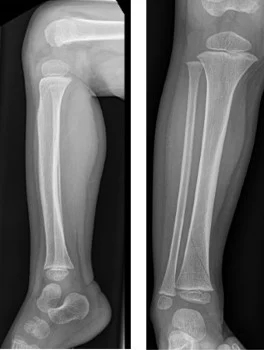
Toddler’s Fracture
Oblique, Non-Displaced Tibial Shaft Fracture
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker or stirrup splint
- Child may bear weight in pneumatic walker, but they cannot bear weight in stirrup splint
- May place in long-leg cast if necessary
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Toddler’s Fracture
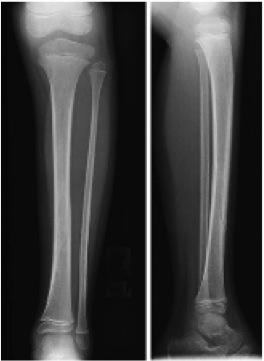
Non-Displaced Tibia Fracture
Immobilization
- Long-Leg Posterior Splint +/- Short-Leg Stirrup (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Non-Displaced Tibia Shaft Fracture
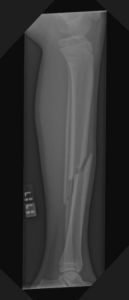
Displaced Tibia Fracture
Immobilization
- Long-Leg Posterior Splint +/- Short-Leg Stirrup (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho
Displaced Tibial Shaft Fracture
Proximal Fibula (with Normal Ankle)
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker (Weight bear as tolerated)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Proximal Fibula Fracture
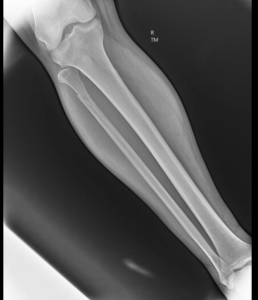
Distal Fibula Fracture
Non-Displaced, Physeal or Epiphyseal Avulsion
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho or Sports Med
- If skeletally mature obtain stress view (external rotation or gravity stress view) and call Ortho for review
Ankle Fractures
Triplane Fracture
Complex Distal Tiba Salter Harris IV Fracture
Immobilization
- Short leg posterior splint (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho – May need CT scan
Triplane Fracture
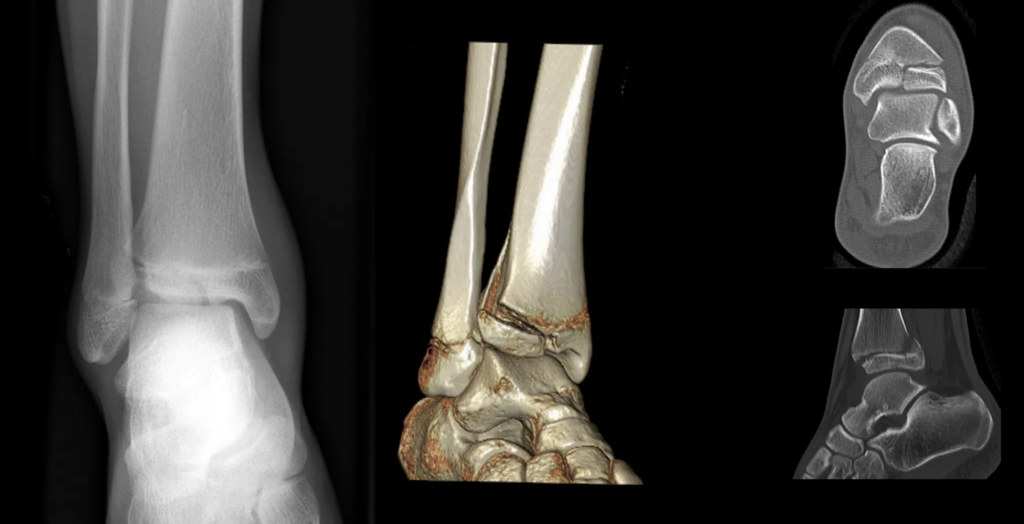
Tillaux Fracture
Distal Tibia Salter Harris III Fracture
Immobilization
- Short leg posterior splint (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho – May need CT scan
Tillaux Fracture
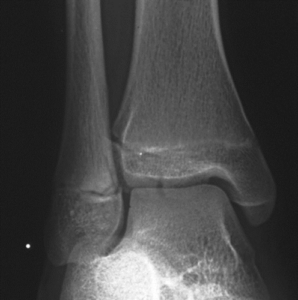
Ankle Sprain
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker (Weight bear as tolerated)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Sports Med
Foot Fractures
Non-Displaced Tarsal Fracture
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker (Weight bear as tolerated)
- Short leg posterior splint if Pneumatic Walker not available (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
- Follow up with Ortho
Non-Displaced Tarsal Fracture
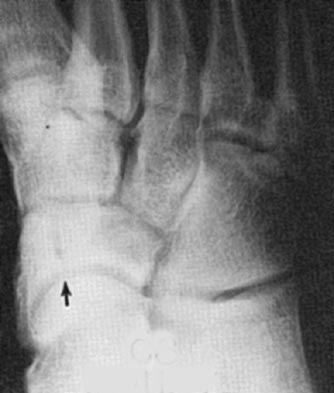
Any Metatarsal Fracture
Immobilization
- Pneumatic walker (Weight bear as tolerated)
- Short leg posterior splint if Pneumatic Walker not available (Non-weight bearing)
Follow Up
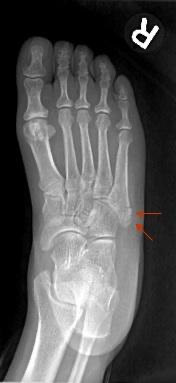
- Follow up with Ortho (Especially important with proximal 5th metatarsal fractures – they are at risk for difficulty healing)
5th Metatarsal Fracture
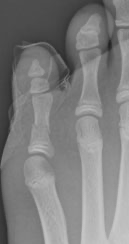
Toe Fractures
Immobilization
- Cast Shoe +/- Buddy Taping (OK for weight-bearing if possible – but difficult to bear weight with fractures of the great toe)
Follow Up
- Call to Ortho if Seymour fracture
- Follow up with Ortho if reduction required or involves great toe
- All others can follow up with PCP
- Any bleeding under the nail associated with fracture, especially great toe, consider and treat as an open fracture and prescribe antibiotics for home
5th Toe Fracture
Toe Dislocation
Immobilization
- ED to attempt reduction with digital block for acute dislocation
Follow Up
- Call Ortho for unsuccessful reduction or chronic dislocation